In this program we will clear the concept of polymorphism, that how a single function can work for all classes.
The code is given below
//Code Starts
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
class apply{
public:
virtual void brak()=0; // Creating pure virtual function
};
class bike:public apply { //inheriting a class
public:
virtual void brak()
{
cout<<"Break applied to Bike"<<endl;
}
};
class car: public apply{
public:
virtual void brak() //calling virtual function
{
cout<<"Break applied to Car"<<endl;
}
};
class truck: public apply{
public:
virtual void brak()
{
cout<<"Break applid to Truck"<<endl;
}
};
class train: public apply
{
public:
virtual void brak()
{
cout<<"Break applied to Train";
}
};
void stop(apply* abc[], int size) //creating a function of data type void
{
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
abc[i] -> brak(); //storing value in pure virtual function by this pointer ->
}
}
int main()
{
int size=4;
apply* xyz[size];
xyz[0]= new bike(); // calling class at 0 index of loop
xyz[1]= new car();
xyz[2]= new truck();
xyz[3]= new train();
stop(xyz,size); //calling void function
getch();
}
//Code Ends
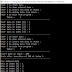
OUTPUT:

The code is given below
//Code Starts
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
class apply{
public:
virtual void brak()=0; // Creating pure virtual function
};
class bike:public apply { //inheriting a class
public:
virtual void brak()
{
cout<<"Break applied to Bike"<<endl;
}
};
class car: public apply{
public:
virtual void brak() //calling virtual function
{
cout<<"Break applied to Car"<<endl;
}
};
class truck: public apply{
public:
virtual void brak()
{
cout<<"Break applid to Truck"<<endl;
}
};
class train: public apply
{
public:
virtual void brak()
{
cout<<"Break applied to Train";
}
};
void stop(apply* abc[], int size) //creating a function of data type void
{
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
abc[i] -> brak(); //storing value in pure virtual function by this pointer ->
}
}
int main()
{
int size=4;
apply* xyz[size];
xyz[0]= new bike(); // calling class at 0 index of loop
xyz[1]= new car();
xyz[2]= new truck();
xyz[3]= new train();
stop(xyz,size); //calling void function
getch();
}
//Code Ends
OUTPUT:










0 comments:
Post a Comment